Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Friday, 17 May 2024
'Meter' p4 Searchterm 'Meter' found in 54 articles 2 terms [ • ] - 52 definitions [• ] Result Pages : • 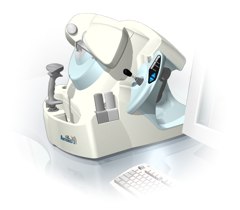 From Ultralink LLC;
From Ultralink LLC;'Artemis is a very high frequency (VHF) ultrasound eye scanner. In use, the patient leans forward placing their head onto an adjustable headrest. The headrest's unique design permits the patient to pull away quickly from the scanner if desired. An eyecup filled with a saline-based interface fluid couples the ultrasound signal to the eye, while a precision mechanism moves the transducer past the front of the eye. During the accurately controlled arc motion of the transducer, which lasts less than one second, many thousands of ultrasound samples are digitized. Following a scan, signal analysis is performed on a PC-compatible microcomputer, and the data are available for immediate viewing on an LCD monitor or disk storage. Artemis is very flexible; many adjustments to the scanning parameters are possible to customize the scan to your clinical needs. Functions are provided for centering the scan about the optical axis of the eye. The starting location of the scans as well as the extent can be varied as desired, to view image planes through the eye at different angles.' See also Ultrasound Biomicroscopy, A-Mode and A-Scan. Further Reading: News & More:
•
This coefficient is a quantification of the energy intensity loss of waves (electromagnetic or mechanical) due to attenuation.
In ultrasound imaging it is the relative energy intensity loss per traveled centimeter. The ultrasound attenuation coefficient is measured in units of dB/cm. The attenuation coefficient in soft tissues is nearly proportional to the ultrasound frequency. The attenuation coefficient is doubled when the frequency is doubled. This coefficient (dB/cm) divided by the frequency (MHz) is almost constant in a given tissue.
•
blood: 0.2 MHz x dB/cm;
•
fatty tissue: 0.6 MHz x dB/cm;
•
liver: 0.9 MHz x dB/cm;
•
soft tissue: 0.5-1.0 MHz x dB/cm.
•
From Bracco Research SA, Geneva, Switzerland,
BR14 is a new experimental ultrasound contrast agent, consisting of bubbles containing a high molecular weight filling gas enclosed by a flexible phospholipid monolayer shell a few nanometers thick. This agent shows significant non-linear scattering and agent modification even at low insonation pressures, the detection pulses used did not destroy the contrast bubbles. The results obtained with HPD before the release burst show that the BR14 bubbles are efficient scatterers that can be modified and, thus, detected by low power insonation.
Drug Information and Specification
RESEARCH NAME
BR14
DEVELOPER
DEVELOPMENT STAGE
Preclinical
APPLICATION
-
TYPE
Microbubble
-
CHARGE
Negative
Perfluorobutane
MICROBUBBLE SIZE
Mean size 3μm, 95% < 10μm
DO NOT RELY ON THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HERE, THEY ARE
NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PACKAGE INSERT! •
The dimension of the ultrasound beam and the transducer array are the origin of the beam width artifact or volume averaging artifact. When the ultrasound beam is wider than the diameter of the lesion being scanned, normal tissues which lie immediately adjacent to the lesion arc included within the beam width, and their echotexture is averaged in with that of the lesion. Thus, what appears to be the echogenicity of the lesion is really that of the lesion plus the averaged normal tissues. Because of volume averaging, cystic lesions may falsely appear to be solid, and some subtle solid lesions may become impossible to distinguish from surrounding normal tissue and, therefore, not identified at all. See also Ultrasound Picture and Vector Array Transducer. •
For the flowprobe a vessel is positioned between transducers which generate wide beams of ultrasound to fully illuminate the vessel. The ultrasound beams alternately intersect the flowing blood in upstream and downstream directions. The flowmeter derives an accurate measure of the changes in transit time influenced by the motion of the blood. See also Bi-directional Flow. Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]




