Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Sunday, 19 May 2024
'Array' p3 Searchterm 'Array' found in 71 articles 9 terms [ • ] - 62 definitions [• ] Result Pages : •
Duplex ultrasonography (duplex scan) consists of two ultrasound modalities to study blood flow and the perivascular tissue. This includes B-mode / gray scale imaging used in combination with spectral Doppler / pulsed-wave Doppler. The real-time visualization of the vessels and tissue by the B-mode component improves the PW Doppler positioning and the direction of blood flow can be inferred. The angle between the direction of the PW Doppler signal and the estimated direction of blood flow can be measured. Duplex techniques are available on phased array, linear array, and mechanical scanners. A phased array probe is able to create nearly simultaneous images and flow information. A linear array transducer can also do this if the Doppler probe is attached separately to one end of the scanhead. A mechanical transducer freeze the image; the crystals must be static to produce a Doppler image. The first two transducers are therefore the best choice for Duplex. See also Compound B-Mode, and Duplex Scanner. Further Reading: News & More:
• 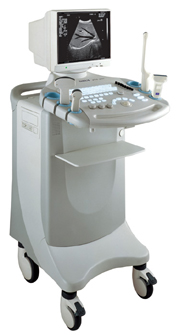 From SIUI Inc.;
From SIUI Inc.;'Dedicated to ultrasound industry, Shantou Institute of Ultrasonic Instruments, Inc. (SIUI) has launched Apogee 3500, the Digital Color Doppler Ultrasound Imaging System. With latest imaging technologies, high-definition image quality and excellent practical functions, the Apogee 3500 offers optimal solutions for clinical ultrasonic examination.' 'The Apogee 3500 is available with many high-density, super broadband and multi-frequency probes, such as convex, micro-convex, linear, vaginal, rectal and phased array probes, which are widely applied for different clinical diagnoses, including abdomen (liver, kidney, gall-bladder, pancreas), gynecology (uterus, ovary), obstetrics (early pregnancy, basic OB, complete OB, multi gestation, fetal echo), cardiology (adult and pediatric cardiology), small parts (thyroid, galactophore, testicles, neonate), peripheral vascular and prostate.'
Device Information and Specification
CONFIGURATION
Normal system, color - gray scale(256)
Linear, convex and phased array
PROBES STANDARD
2.0 MHz ~ 12.0 MHz, broad band, tri-frequency
B-mode (B, 2B, 4B), M-mode, B/M-mode, real-time compound imaging, panoramic imaging, trapezoidal imaging (linear probes), spectrum Doppler (PWD and CWD), color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI), color power angio (CPA), tissue harmonic imaging (THI)
IMAGING OPTIONS
Real-time ZOOM, zoom rate and position selectable
OPTIONAL PACKAGE
H*W*D m
1.29 * 0.52 * 0.75
WEIGHT
110 kg
POWER REQUIREMENT
AC 220V/110V, 50Hz/60Hz
POWER CONSUMPTION
0.6 KVA
•
The wider the ultrasound beam, the more severe the problem with volume averaging and the beam-width artifact, to avoid this, the ultrasound beam can be shaped with lenses.
Different possibilities to focus the beam:
•
Mechanical focusing is performed by placing an acoustic lens on the surface of the transducer or using a transducer with a concave face.
•
Electronic focusing uses multiple phased array (annular or linear) elements, sequentially fired to focus the beam.
Conventional multi-element transducers are electronically focused in order to minimize beam width. This transducer type can be focused electronically only along the long axis of the probe where there are multiple elements, along the short axis (elevation axis) are conventional transducers only one element wide. Electronic focusing in any axis requires multiple transducer elements arrayed along that axis. Short axis focusing of conventional multi-element transducers requires an acoustic lens which has a fixed focal length. For operation at frequencies at or even above 10 MHz, quantization noise reduces contrast resolution. Digital beamforming gives better control over time delay quantization errors. In digital beamformers the delay accuracy is improved, thus allowing higher frequency operation. In analog beamformers, delay accuracy is in the order of 20 ns. Phased beamformers are suitable to handle linear phased arrays and are used for sector formats such as required in cardiography to improve image quality. Beamforming in ultrasound instruments for medical imaging uses analog delay lines. The signal from each individual element is delayed in order to steer the beam in the desired direction and focuses the beam. The receive beamformer tracks the depth and focuses the receive beam as the depth increases for each transmitted pulse. The receive aperture increase with depth. The lateral resolution is constant with depth, and decreases the sensitivity to aberrations in the imaged tissue. A requirement for dynamic control of the used elements is given. Since often a weighting function (apodization) is used for side lobe reduction, the element weights also have to be dynamically updated with depth. See also Huygens Principle. •
A curved or curvilinear array transducer is similar to a linear array except that the image created has a sector-type format. A curvilinear array gives a large footprint and near field with a wide sector. Usually, curved transducers are described by the radius of curvature in mm. The transducer elements control the characteristics and direction of the sound beam. Curvilinear transducers have a wider field of view from the transducer face. Sector scanners are most useful for cardiac ultrasound examinations where the beam is directed between the ribs to image the heart. Also called convex transducer. •
A linear probe contains one or more acoustic linear array transducer elements arranged in a line to send pulses of sound into a material. The linear array gives a large probe surface (footprint) and near field. In Doppler mode, a linear probe operates a subset of its elements as a linear phased array and can thus steer the Doppler beam at a selected angle to the imaging beam. This is a popular configuration for peripheral vascular and perivascular scanning.
Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]




