Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Friday, 17 May 2024
'Phase' p2 Searchterm 'Phase' found in 77 articles 4 terms [ • ] - 73 definitions [• ] Result Pages : •
From Bayer Schering Pharma AG:
Available in Europe since 1996 and in Japan since 1999. Currently, the marketing situation is unclear. Levovist® is a first generation USCA consisting of galactose (milk sugar) ground into tiny crystals whose irregular surfaces act as nidation sites on which air pockets form when it is suspended in water, much as soda water bubbles form at small irregularities on the surface of the glass. A trace of palmitic acid is added as a surfactant to stabilize the resultant microbubbles. When Levovist® dissolves in blood, air trapped inside the galactose is released as free gas bubbles. These bubbles have a weak encapsulating shell and are easily destroyed by ultrasound. Different contrast ultrasonography methods have been developed since the introduction of Levovist®. Initially, Levovist® was an echo contrast medium for improving sensitivity in color Doppler and Power Doppler examinations, but was found to suffer from significant blooming, making it difficult to observe small blood vessels. However, Levovist® improves the accuracy of echocardiographic examinations in such indications as assessment of left ventricular function. In addition to their vascular phase, some ultrasound contrast agents (USCAs) can exhibit a tissue- or organ-specific phase. Levovist® can accumulate within the liver and the spleen for up to 20 min once it has disappeared from the blood pool and improves the detectability of focal liver lesions and allows more reliable control of interventional tumor treatments. Varied types of information can be obtained by applying contrast imaging at different times after the injection using Levovist® in both the arterial phase and the late organ-specific phase. 1 g Levovist® granules contain 999 mg D-galactose and 1 mg palmitic acid. Brand names in other countries: Levovist/Levograf
Drug Information and Specification
RESEARCH NAME
SHU 508A
DEVELOPER
INDICATION
APPLICATION
Intravenous injection
TYPE
Microbubble
Galactose/Palmitic acid
CHARGE
Negative
Air
MICROBUBBLE SIZE
95% < 10μm
PRESENTATION
Vials of 2.5 g and 4.0 g incl. one plastic ampoule containing 20 ml water for injection, one mini-spike and one disposable syringe of 20 ml
STORAGE
Room temp 15−30°C
PREPARATION
Reconstitute with 5 to 17 ml water
DO NOT RELY ON THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HERE, THEY ARE
NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PACKAGE INSERT! •
A liver sonography is a diagnostic tool to image the liver and adjoining upper abdominal organs such as the gallbladder, spleen, and pancreas. Deeper structures such as liver and pancreas are imaged at a lower frequency 1-6 MHz with lower axial and lateral resolution but greater penetration. The diagnostic capabilities in this area can be limited by gas in the bowel scattering the sound waves. The application of microbubbles may be useful for detection of liver lesions and for lesion characterization. Some microbubbles have a liver-specific post vascular phase where they appear to be taken up by the reticuloendothelial system (RES). Dynamic contrast enhanced scans in a similar way as with CT or MRI can be used to studying the arterial, venous and tissue phase. After a bolus injection, early vascular enhancement is seen at around 30sec in arterialized lesions (e.g., hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC), focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)). Later enhancement is typical of hemangiomas with gradually filling towards the center. In the late phase at around 90sec, HCCs appear as defects against the liver background. Most metastases are relatively hypovascular and so do not show much enhancement and are seen as signal voids in the different phases. Either with an intermittent imaging technique or by continuous scanning in a nondestructive, low power mode, characteristic time patterns can be used to differentiate lesions. See also Medical Imaging, B-Mode, High Intensity Focused Ultrasound, Ultrasound Safety and Contrast Medium. Further Reading: Basics:
News & More:
•
From Bayer Schering Pharma AG:
Sonovist® (sometimes found as Sonavist) is an investigational ultrasound contrast agent with a biodegradable synthetic capsule filled with sulphur hexafluoride. The biodegradable shell of Sonovist is so stable that it can be taken up by Kupffer cells of the reticuloendothelial system or accumulate in the sinusoids. Therefore, Sonovist® has an additional hepato-splenic parenchymal phase following the blood pool phase, analog to the superparamagnetic iron oxide agents used in liver MRI. The microbubbles are stationary in this phase and generate no conventional Doppler signals. This tissue-specific phase has a variable duration and can be imaged by bubble specific imaging modes.
Drug Information and Specification
RESEARCH NAME
SHU 563A
DEVELOPER
INDICATION
APPLICATION
Intravenous
TYPE
Microbubble
Cyanoacrylate (polymer sheIl)
CHARGE
-
Sulphur hexafluoride
MICROBUBBLE SIZE
-
PRESENTATION
-
STORAGE
-
PREPARATION
-
DO NOT RELY ON THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HERE, THEY ARE
NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PACKAGE INSERT! • 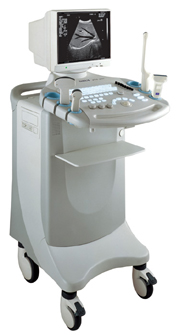 From SIUI Inc.;
From SIUI Inc.;'Dedicated to ultrasound industry, Shantou Institute of Ultrasonic Instruments, Inc. (SIUI) has launched Apogee 3500, the Digital Color Doppler Ultrasound Imaging System. With latest imaging technologies, high-definition image quality and excellent practical functions, the Apogee 3500 offers optimal solutions for clinical ultrasonic examination.' 'The Apogee 3500 is available with many high-density, super broadband and multi-frequency probes, such as convex, micro-convex, linear, vaginal, rectal and phased array probes, which are widely applied for different clinical diagnoses, including abdomen (liver, kidney, gall-bladder, pancreas), gynecology (uterus, ovary), obstetrics (early pregnancy, basic OB, complete OB, multi gestation, fetal echo), cardiology (adult and pediatric cardiology), small parts (thyroid, galactophore, testicles, neonate), peripheral vascular and prostate.'
Device Information and Specification
CONFIGURATION
Normal system, color - gray scale(256)
Linear, convex and phased array
PROBES STANDARD
2.0 MHz ~ 12.0 MHz, broad band, tri-frequency
B-mode (B, 2B, 4B), M-mode, B/M-mode, real-time compound imaging, panoramic imaging, trapezoidal imaging (linear probes), spectrum Doppler (PWD and CWD), color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI), color power angio (CPA), tissue harmonic imaging (THI)
IMAGING OPTIONS
Real-time ZOOM, zoom rate and position selectable
OPTIONAL PACKAGE
H*W*D m
1.29 * 0.52 * 0.75
WEIGHT
110 kg
POWER REQUIREMENT
AC 220V/110V, 50Hz/60Hz
POWER CONSUMPTION
0.6 KVA
•
The wider the ultrasound beam, the more severe the problem with volume averaging and the beam-width artifact, to avoid this, the ultrasound beam can be shaped with lenses.
Different possibilities to focus the beam:
•
Mechanical focusing is performed by placing an acoustic lens on the surface of the transducer or using a transducer with a concave face.
•
Electronic focusing uses multiple phased array (annular or linear) elements, sequentially fired to focus the beam.
Conventional multi-element transducers are electronically focused in order to minimize beam width. This transducer type can be focused electronically only along the long axis of the probe where there are multiple elements, along the short axis (elevation axis) are conventional transducers only one element wide. Electronic focusing in any axis requires multiple transducer elements arrayed along that axis. Short axis focusing of conventional multi-element transducers requires an acoustic lens which has a fixed focal length. For operation at frequencies at or even above 10 MHz, quantization noise reduces contrast resolution. Digital beamforming gives better control over time delay quantization errors. In digital beamformers the delay accuracy is improved, thus allowing higher frequency operation. In analog beamformers, delay accuracy is in the order of 20 ns. Phased beamformers are suitable to handle linear phased arrays and are used for sector formats such as required in cardiography to improve image quality. Beamforming in ultrasound instruments for medical imaging uses analog delay lines. The signal from each individual element is delayed in order to steer the beam in the desired direction and focuses the beam. The receive beamformer tracks the depth and focuses the receive beam as the depth increases for each transmitted pulse. The receive aperture increase with depth. The lateral resolution is constant with depth, and decreases the sensitivity to aberrations in the imaged tissue. A requirement for dynamic control of the used elements is given. Since often a weighting function (apodization) is used for side lobe reduction, the element weights also have to be dynamically updated with depth. See also Huygens Principle. Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]




