Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Monday, 13 May 2024
'Real' p3 Searchterm 'Real' found in 60 articles 3 terms [ • ] - 57 definitions [• ] Result Pages : • 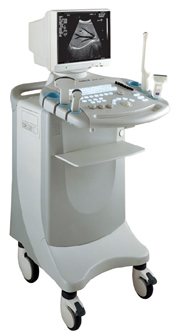 From SIUI Inc.;
From SIUI Inc.;'Incorporating the latest advances in technology, the CTS-6000 digital B/W ultrasound system provides exceptional imaging quality and complete diagnostic capabilities. It is equipped with extensive analysis package, super broadband multifrequency probes and disk storage capacity, a complete system that fully meets different clinical needs. CTS-6000 sets a new standard for digital ultrasound imaging.'
Device Information and Specification
CONFIGURATION
Normal system, 12-inch high-resolution non-interlace monitor , Tri-probe connector
Linear and convex
PROBES STANDARD
1 * Super broadband linear probe L7S34, 1 * super broadband micro-convex probe C3L60, 1 * super broadband micro-convex probe C3120;
IMAGING OPTIONS
Real ZOOM, max. zoomx4.0, position selectable
H*W*D m
1.28 * 0.48 * 0.72
WEIGHT
98kg (main unit)
POWER REQUIREMENT
AC 220V/110V, 50Hz/60Hz
POWER CONSUMPTION
0.43 KVA
•
The earliest introduction of vascular ultrasound contrast agents (USCA) was by Gramiak and Shah in 1968, when they injected agitated saline into the ascending aorta and cardiac chambers during echocardiographic to opacify the left heart chamber. Strong echoes were produced within the heart, due to the acoustic mismatch between free air microbubbles in the saline and the surrounding blood.
•
In 1880 the Curie brothers discovered the piezoelectric effect in quartz. Converse piezoelectricity was mathematically deduced from fundamental thermodynamic principles by Lippmann in 1881.
•
In 1917, Paul Langevin (France) and his coworkers developed an underwater sonar system (called hydrophone) that uses the piezoelectric effect to detect submarines through echo location.
•
In 1935, the first RADAR system was produced by the British physicist Robert Watson-Wat. Also about 1935, developments began with the objective to use ultrasonic power therapeutically, utilizing its heating and disruptive effects on living tissues. In 1936, Siemens markets the first ultrasonic therapeutic machine, the Sonostat.
•
Shortly after the World War II, researchers began to explore medical diagnostic capabilities of ultrasound. Karl Theo Dussik (Austria) attempted to locate the cerebral ventricles by measuring the transmission of ultrasound beam through the skull. Other researchers try to use ultrasound to detect gallstones, breast masses, and tumors. These first investigations were performed with A-mode.
•
Shortly after the World War II, researchers in Europe, the United States and Japan began to explore medical diagnostic capabilities of ultrasound. Karl Theo Dussik (Austria) attempted to locate the cerebral ventricles by measuring the transmission of ultrasound beam through the skull. Other researchers, e.g. George Ludwig (United States) tried to use ultrasound to detect gallstones, breast masses, and tumors. This first experimentally investigations were performed with A-mode. Ultrasound pioneers contributed innovations and important discoveries, for example the velocity of sound transmission in animal soft tissues with a mean value of 1540 m/sec (still in use today), and determined values of the optimal scanning frequency of the ultrasound transducer.
•
In the early 50`s the first B-mode images were obtained. Images were static, without gray-scale information in simple black and white and compound technique. Carl Hellmuth Hertz and Inge Edler (Sweden) made in 1953 the first scan of heart activity. Ian Donald and Colleagues (Scotland) were specialized on obstetric and gynecologic ultrasound research. By continuous development it was possible to study pregnancy and diagnose possible complications.
•
After about 1960 two-dimensional compound procedures were developed. The applications in obstetric and gynecologic ultrasound boomed worldwide from the mid 60's with both, A-scan and B-scan equipment. In the late 60's B-mode ultrasonography replaced A-mode in wide parts.
•
In the 70's gray scale imaging became available and with progress of computer technique ultrasonic imaging gets better and faster.
•
•
In the 90's, high resolution scanners with digital beamforming, high transducer frequencies, multi-channel focus and broad-band transducer technology became state of the art. Optimized tissue contrast and improved diagnostic accuracy lead to an important role in breast imaging and cancer detection. Color Doppler and Duplex became available and sensitivity for low flow was continuously improved.
•
Actually, machines with advanced ultrasound system performance are equipped with realtime compound imaging, tissue harmonic imaging, contrast harmonic imaging, vascular assessment, matrix array transducers, pulse inversion imaging, 3D and 4D ultrasound with panoramic view.
•
Ultrasound is an ideal tool to examine the joints and surrounding soft tissues like tendons, ligaments and joint linings. Musculoskeletal and joint sonography is sensitive, without radiation exposure, easy accessible, quick, and has high patient tolerability with relatively low cost. A real-time scanner allow the dynamic assessment of the musculoskeletal system and a specific examination for each patient. In addition, joint aspiration and injection accuracy can be improved. Probes with high frequency improve the image resolution and allow visualization of fine anatomic structures of the small parts. As musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) is very operator dependent, experience and training is required. Ultrasound is also often used in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. See also Ultrasound Therapy, Real-Time Mode, Artifact and Ultrasound Biomicroscopy. Further Reading: Basics:
•
The elements of a rectangular array transducer (also called matrix transducer) are arranged in a rectangular pattern. Rectangular arrays with unequal rows (e.g. 3, 5, 7) of transducer elements are in real 2D (two-dimensional), but they are termed 1.5D, because the number of rows is much less than the number of columns. Their main advantage is electronic focusing even in the elevation plane (z-plane). The transducers that are termed 2D have an equal number of rows and columns. 2D transducers have the potential to provide real-time 3D ultrasound imaging without moving the transducer. Active matrix array transducers have several elements in the short axis and in addition multiple elements along the long axis. This allows electronic focusing in both axes, resulting in a narrower elevation axis beam width in the near field and far field. •  From Medison Co.,Ltd.;
From Medison Co.,Ltd.;'It's the dawn of a new Evolution in affordable digital color ultrasound At Medison, we have a history of innovation. We were the first to make the leap to the third dimension when we introduced our groundbreaking digital 3D ultrasound platform with Live 3D™ technology in 1998, making it possible to capture true 3D volume data in real-time. Today, we're proud to introduce the SONOACE , the world's first true 3D color ultrasound system designed to bring the power of real-time 3D imaging to women's health specialists at a breakthrough price.' 'SONOACE 8000 Live PRIME, the true 3D ultrasound system designed to bring the power of live 3D in your hands. SONOACE 8000 Live PRIME offers superior image quality thanks to our new C-Square Technology and newly applied PSAD Beamformer.' Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]




