Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Sunday, 19 May 2024
'Power Doppler' p2 Searchterm 'Power Doppler' found in 34 articles 4 terms [ • ] - 30 definitions [• ] Result Pages : •
(CD) Color Doppler is an ultrasound imaging mode, which visualizes the presence, direction and velocity of flowing blood in a wide range of flow conditions. It provides an estimate of the mean velocity of flow within a vessel by color coding the flow and displaying it superimposed on the 2D gray scale image. The flow direction is arbitrarily assigned the color red or blue, indicating flow toward or away from the transducer. Color (colour, Brit.) Doppler ultrasound is capable of evaluating a wider area than other Doppler modes than for example Duplex or power Doppler, and therefore makes it less likely to miss flow abnormalities. It is also easier to interpret. Color flow is not as precise as conventional Doppler and is best used to scan a larger area and then use conventional Doppler for detailed analysis at a site of potential flow abnormality. Adjustments for color Doppler in case of too much color: Adjustments for color Doppler in case of not enough color:
•
increased color gain;
•
decrease color velocity scale;
•
adjust scanning plane and angle to flow;
•
decrease sample box size;
•
evaluation of chosen filter.
See also Color Power Doppler, Autocorrelation, Color Priority, Triplex Exam and Color Saturation. Further Reading: Basics:
News & More:
• 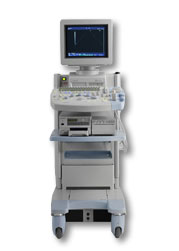 From Hitachi Medical Corporation (HMC), sales, marketing and service in the US by Hitachi Medical Systems America Inc.
From Hitachi Medical Corporation (HMC), sales, marketing and service in the US by Hitachi Medical Systems America Inc.The HI VISION™ 5500 - EUB-5500 fully digital ultrasound system delivers the latest generation of signal processing technology, sophisticated transducer design, and a host of features and options for advanced imaging capabilities across a wide range of clinical situations. This system is compatible with all Pentax ultrasound endoscopes.
Device Information and Specification
APPLICATIONS
Abdominal, brachytherapy/cryotherapy, breast, cardiac, dedicated biopsy, endoscopic, intraoperative, laparoscopic, musculoskeletal, OB/GYN, pediatric, small parts, urologic, vascular
CONFIGURATION
Compact system
Five frequency (except mini-probes)
Linear, convex, radial, miniradial/miniprobe, biplane, phased array, echoendoscope longitudinal, echoendoscope radial
3 modes of dynamic tissue harmonic imaging (dTHI), pulsed wave Doppler, continuous wave Doppler, color flow imaging, power Doppler, directional power Doppler, color flow angiography, real-time Doppler measurements
IMAGING OPTIONS
3RD generation color artifact suppression
OPTIONAL PACKAGE
STORAGE, CONNECTIVITY, OS
Patient and image database management system, HDD, FDD, MOD, CD-ROM, Network, DICOM 3.0, Windows XP
DATA PROCESSING
H*W*D m (inch.)
1.40 x 0.51 x 0.79 (55 x 20 x 31)
WEIGHT
130 kg (286 lbs.)
POWER CONSUMPTION
1.2kVA
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
4096 btu/hr heat output
• 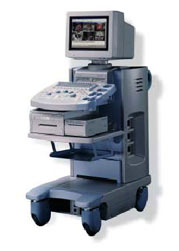 From Hitachi Medical Corporation (HMC), sales, marketing and service in the US by Hitachi Medical Systems America Inc.;
From Hitachi Medical Corporation (HMC), sales, marketing and service in the US by Hitachi Medical Systems America Inc.;Powerful, flexible, and fast, the HI VISION™ 8500 - EUB-8500 diagnostic ultrasound scanner combines leading edge technologies with user-oriented operation for exceptional imaging and functionality. Available exclusively on the 8500, SonoElastography provides a new perspective on the physical properties of tumors and masses by determining and displaying the relative stiffness of tissue. Device Information and Specification
APPLICATIONS
Abdominal, brachytherapy/cryotherapy, breast, cardiac, dedicated biopsy, endoscopic, intraoperative, laparoscopic, musculoskeletal, OB/GYN, pediatric, small parts, urologic, vascular
CONFIGURATION
Compact system
RANGE OF PROBE TYPE
Linear, convex, radial, biplane, phased array, echoendoscope longitudinal, echoendoscope radial
PROBE FREQUENCIES
Linear: 5.0-13 MHz, convex: 2.5-7.5 MHz, phased:
2.0-7.5 MHz, sector: 2.0-7.5 MHz
4 Modes of dynamic tissue harmonic imaging (dTHI), pulsed wave Doppler, continuous wave Doppler, color flow imaging, power Doppler, directional power Doppler, color flow angiography, real-time Doppler measurements, quantitative tissue Doppler
IMAGING OPTIONS
HI COMPOUND imaging,
HI RES adaptive imaging, wideband pulse inversion imaging (WPI), Raw Data Freeze
OPTIONAL PACKAGE
IMAGING ENHANCEMENTS
3RD generation color artifact suppression
STORAGE, CONNECTIVITY, OS
Patient and image database management system, HDD, FDD, MOD, CD-ROM, Network, DICOM 3.0, Windows XP
DATA PROCESSING
Octal beam processing, 12 bit Gigasampling A/D for precise signal reproduction
H*W*D m (inch.)
1.50 * 0.56 * 1.02 (59 x 22 x 40)
WEIGHT
159 kg (351 lbs.)
POWER CONSUMPTION
1.5kVA
•  From Hitachi Medical Corporation (HMC);
From Hitachi Medical Corporation (HMC);The HI VISION™ 6500 - EUB-6500 high resolution digital ultrasound system offers advanced clinical imaging, enhanced operating efficiency, and remarkable clinical flexibility, all in robust and versatile configuration that simply represents a better clinical solution in a variety of real-world, real-work arenas.
Device Information and Specification
APPLICATIONS
Abdominal, brachytherapy/cryotherapy, breast, cardiac, dedicated biopsy, endoscopic, intraoperative, laparoscopic, musculoskeletal, OB/GYN, pediatric, small parts, urologic, vascular
CONFIGURATION
Compact system
Linear, convex, radial, miniradial/miniprobe, biplane, phased array, echoendoscope longitudinal, echoendoscope radial
Tissue Doppler imaging (TDI), pulsed wave Doppler, continuous wave Doppler, color flow imaging, power Doppler, directional power Doppler, color flow angiography, real-time Doppler measurements, 4 modes of dynamic tissue harmonic imaging (dTHI), wideband pulse inversion imaging (WPI)
IMAGING OPTIONS
3RD generation color artifact suppression
OPTIONAL PACKAGE
3D ultrasound, dual omni-directional M-mode display, steerable CW Doppler, dynamic contrast harmonics imaging, stress echo, Pentax EUS and Fujinon Mini-probe
STORAGE, CONNECTIVITY, OS
Patient and image database management system, HDD, FDD, MOD, CD-ROM, Network, DICOM 3.0, Windows XP
DATA PROCESSING
H*W*D m (inch.)
1.40 x 0.51 x 0.79 (55 x 20 x 31)
WEIGHT
130 kg (286 lbs.)
POWER CONSUMPTION
1.2kVA
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
4096 btu/hr heat output
•
Standard scanners allow visualizing microbubbles on conventional gray scale imaging in large vascular spaces. In the periphery, more sensitive techniques such as Doppler or non-linear gray scale modes must be used because of the dilution of the microbubbles in the blood pool. Harmonic power Doppler (HPD) is one of the most sensitive techniques for detecting ultrasound contrast agents. Commonly microbubbles are encapsulated or otherwise stabilized to prolong their lifetime after injection. These bubbles can be altered by exposure to ultrasound pulses. Depending on the contrast agent and the insonating pulse, the changes include deformation or breakage of the encapsulating or stabilizing material, generation of free gas bubbles, reshaping or resizing of gas volumes. High acoustic pressure amplitudes and long pulses increase the changes. However, safety considerations limit the pressure amplitude and long pulses decrease spatial resolution. In addition, lowering the pulse frequency increases destruction of contrast bubbles. However, at low insonation power levels, contrast agent particles resist insonation without detectable changes. Newer agents are more reflective and will usually allow gray scale imaging to be used with the advantages of better spatial resolution, fewer artifacts and faster frame rates. Feasible imaging methods with advantages in specific acoustic microbubble properties: Resonating microbubbles emit harmonic signals at double their resonance frequency. If a scanner is modified to select only these harmonic signals, this non-linear mode produces a clear image or trace. The effect depends on the fact that it is easier to expand a bubble than to compress it so that it responds asymmetrically to a symmetrical ultrasound wave. A special array design allows to perform third or fourth harmonic imaging. This probe type is called a dual frequency phased array transducer. See also Bubble Specific Imaging. Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]




