Medical Ultrasound Imaging
Thursday, 9 May 2024
'Real-Time Transducer' Searchterm 'Real-Time Transducer' found in 19 articles 1 term [ • ] - 2 definitions [• ] - 16 booleans [• ]Result Pages : • Real-Time Transducer
Transducers used for the real-time mode are different than for the A-mode, B-, or M-modes. A linear array transducer with multiple piezoelectric crystal elements that are different arranged and fired, transmits the needed larger sound beam. A subgroup of x adjacent elements (8-16; or more in wide-aperture designs) is pulsed simultaneously; the inner elements pulse delayed with respect to the outer elements. The interference of the x small divergent wavelets generates a focused beam. The delay time determining the focus depth of a real-time transducer can be changed during imaging. Similar delay factors applied during the receiving phase, result in a dynamic focusing effect on the return. This forms a single scan line in the real-time image. To produce the following scan line, another group of x elements is selected by shifting one element position along the transducer array from the previous group. This pattern is then repeated for the groups along the array, in a sequential and repetitive way. Further Reading: Basics: •
Dynamic focusing controls the axial position of the focus of an ultrasound beam. Dynamic focusing is often managed by controlling the phase of the signals detected by a transducer array. See also Real-Time Transducer. •
Real-time mode has been developed to present motion like a movie of the body's inner workings, showing this information at a high rate. The special real-time transducer uses a larger sound beam than for A, B or M-modes. A linear array transducer with multiple crystal elements displays real-time compound B-mode images with up to 100 images per second. At each scan line, one sound pulse is transmitted and all echoes from the surface to the deepest range are received. Then the ultrasound beam moves on to the next scan line position where pulse transmission and echo recording are repeated. See also Compound B-Mode, Pulse Inversion Doppler, and Frame Averaging. Further Reading: News & More:
•  From ALOKA Co., Ltd.;
From ALOKA Co., Ltd.;'A Platform for Digital, Pure-Beam Imaging The high-performance, ALOKA ProSound SSD-3500 utilizes advanced ProSound technologies including: Fully digital beam former A wide dynamic range, 12-bit A/D converter Multi beam processing. The SSD-3500 also helps you achieve more efficient examinations. Its ergonomic, user-friendly design enables you to customize the system according to your specific application needs.'
Device Information and Specification
APPLICATIONS
CONFIGURATION
Compact, portable, dual dynamic display
Color Flow, Power Flow, Spectral Doppler, Real-time Free Angular M-Mode, Tissue Harmonic Imaging, Quint Frequency Imaging, Pure Harmonic Detection
STORAGE, CONNECTIVITY, OS
Data Management Subsystem (iDMS), DICOM-Worklist
DATA PROCESSING
12-bit analog to digital converter
• 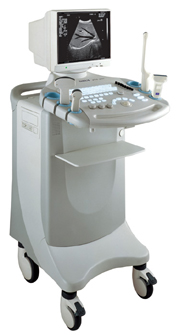 From SIUI Inc.;
From SIUI Inc.;'Dedicated to ultrasound industry, Shantou Institute of Ultrasonic Instruments, Inc. (SIUI) has launched Apogee 3500, the Digital Color Doppler Ultrasound Imaging System. With latest imaging technologies, high-definition image quality and excellent practical functions, the Apogee 3500 offers optimal solutions for clinical ultrasonic examination.' 'The Apogee 3500 is available with many high-density, super broadband and multi-frequency probes, such as convex, micro-convex, linear, vaginal, rectal and phased array probes, which are widely applied for different clinical diagnoses, including abdomen (liver, kidney, gall-bladder, pancreas), gynecology (uterus, ovary), obstetrics (early pregnancy, basic OB, complete OB, multi gestation, fetal echo), cardiology (adult and pediatric cardiology), small parts (thyroid, galactophore, testicles, neonate), peripheral vascular and prostate.'
Device Information and Specification
CONFIGURATION
Normal system, color - gray scale(256)
Linear, convex and phased array
PROBES STANDARD
2.0 MHz ~ 12.0 MHz, broad band, tri-frequency
B-mode (B, 2B, 4B), M-mode, B/M-mode, real-time compound imaging, panoramic imaging, trapezoidal imaging (linear probes), spectrum Doppler (PWD and CWD), color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI), color power angio (CPA), tissue harmonic imaging (THI)
IMAGING OPTIONS
Real-time ZOOM, zoom rate and position selectable
OPTIONAL PACKAGE
H*W*D m
1.29 * 0.52 * 0.75
WEIGHT
110 kg
POWER REQUIREMENT
AC 220V/110V, 50Hz/60Hz
POWER CONSUMPTION
0.6 KVA
Result Pages : |
Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging.com
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
former US-TIP.com
Member of SoftWays' Medical Imaging Group - MR-TIP • Radiology TIP • Medical-Ultrasound-Imaging
Copyright © 2008 - 2024 SoftWays. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Advertise With Us
[last update: 2023-11-06 01:42:00]




